Dual band circular polarization selector using asymmetric SRR mirrors
Visualitza/Obre
Estadístiques de LA Referencia / Recolecta
Inclou dades d'ús des de 2022
Cita com:
hdl:2117/369836
Tipus de documentText en actes de congrés
Data publicació2022
EditorUniversitat Politècnica de Catalunya. Remote Sensing, Antennas, Microwaves and Superconductivity Group (CommSensLab)
Condicions d'accésAccés obert
Llevat que s'hi indiqui el contrari, els
continguts d'aquesta obra estan subjectes a la llicència de Creative Commons
:
Reconeixement-NoComercial-SenseObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional
Abstract
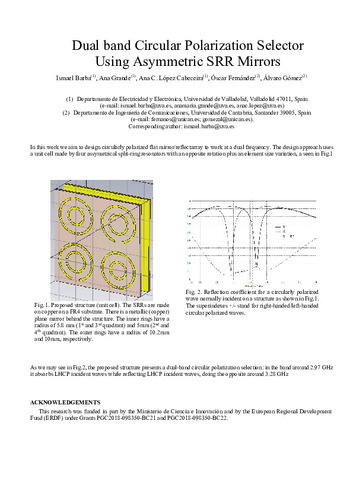
In this work we aim to design circularly polarized flat mirror/reflectarray to work at a dual frequency. The design approach uses
a unit cell made by four assymetrical split-ring resonators with an opposite rotation plus an element size variation, a seen in Fig.1
Fig. 1. Proposed structure (unit cell). The SRRs are made
on copper on a FR4 substrate. There is a metallic (copper)
plane mirror behind the structure. The inner rings have a
radius of 5.8 mm (1st and 3rd quadrant) and 5mm (2nd and
4th quadrant). The outer rings have a radius of 10.2mm
and 10mm, respectively.
As we may see in Fig.2, the proposed structure presents a dual-band circular polarization selection: in the band around 2.97 GHz
it absorbs LHCP incident waves while reflecting LHCP incident waves, doing the opposite around 3.28 GHz
Fig. 2. Reflection coefficient for a circularly polarized
wave normally incident on a structure as shown in Fig.1.
The superindexes +/- stand for right-handed/left-handed
circular polarized waves.
CitacióBarba, I. [et al.]. Dual band circular polarization selector using asymmetric SRR mirrors. A: EIEC 2022. "XIV Iberian Meeting on Computational Electromagnetics". Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya. Remote Sensing, Antennas, Microwaves and Superconductivity Group (CommSensLab), 2022,
| Fitxers | Descripció | Mida | Format | Visualitza |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EIEC_2022_20_Dual band Circular Polarization.pdf | 303,8Kb | Visualitza/Obre |


